Java 基础IO - 实例
磁盘操作
File 类可以用于表示文件和目录的信息,但是它不表示文件的内容。
递归地列出一个目录下所有文件:
public static void listAllFiles(File dir) {
if (dir == null || !dir.exists()) {
return;
}
if (dir.isFile()) {
System.out.println(dir.getName());
return;
}
for (File file : dir.listFiles()) {
listAllFiles(file);
}
}
字节操作
实现文件复制
public static void copyFile(String src, String dist) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dist);
byte[] buffer = new byte[20 * 1024];
// read() 最多读取 buffer.length 个字节
// 返回的是实际读取的个数
// 返回 -1 的时候表示读到 eof,即文件尾
while (in.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length) != -1) {
out.write(buffer);
}
in.close();
out.close();
}
装饰者模式
Java I/O 使用了装饰者模式来实现。以 InputStream 为例,
- InputStream 是抽象组件;
- FileInputStream 是 InputStream 的子类,属于具体组件,提供了字节流的输入操作;
- FilterInputStream 属于抽象装饰者,装饰者用于装饰组件,为组件提供额外的功能。例如 BufferedInputStream 为 FileInputStream 提供缓存的功能。
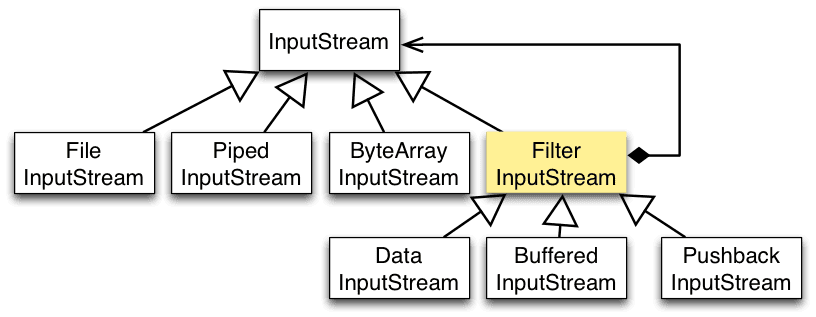
实例化一个具有缓存功能的字节流对象时,只需要在 FileInputStream 对象上再套一层 BufferedInputStream 对象即可。
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
DataInputStream 装饰者提供了对更多数据类型进行输入的操作,比如 int、double 等基本类型。
字符操作
编码与解码
编码就是把字符转换为字节,而解码是把字节重新组合成字符。
如果编码和解码过程使用不同的编码方式那么就出现了乱码。
- GBK 编码中,中文字符占 2 个字节,英文字符占 1 个字节;
- UTF-8 编码中,中文字符占 3 个字节,英文字符占 1 个字节;
- UTF-16be 编码中,中文字符和英文字符都占 2 个字节。
UTF-16be 中的 be 指的是 Big Endian,也就是大端。相应地也有 UTF-16le,le 指的是 Little Endian,也就是小端。
Java 使用双字节编码 UTF-16be,这不是指 Java 只支持这一种编码方式,而是说 char 这种类型使用 UTF-16be 进行编码。char 类型占 16 位,也就是两个字节,Java 使用这种双字节编码是为了让一个中文或者一个英文都能使用一个 char 来存储。
String
String 可以看成一个字符序列,可以指定一个编码方式将它编码为字节序列,也可以指定一个编码方式将一个字节序列解码为 String。
String str1 = "中文";
byte[] bytes = str1.getBytes("UTF-8");
String str2 = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(str2);
在调用无参数 getBytes() 方法时,默认的编码方式不是 UTF-16be。双字节编码的好处是可以使用一个 char 存储中文和英文,而将 String 转为 bytes[] 字节数组就不再需要这个好处,因此也就不再需要双字节编码。getBytes() 的默认编码方式与平台有关,一般为 UTF-8。
byte[] bytes = str1.getBytes();
Reader 与 Writer
不管是磁盘还是网络传输,最小的存储单元都是字节,而不是字符。但是在程序中操作的通常是字符形式的数据,因此需要提供对字符进行操作的方法。
- InputStreamReader 实现从字节流解码成字符流;
- OutputStreamWriter 实现字符流编码成为字节流。
实现逐行输出文本文件的内容
public static void readFileContent(String filePath) throws IOException {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String line;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
// 装饰者模式使得 BufferedReader 组合了一个 Reader 对象
// 在调用 BufferedReader 的 close() 方法时会去调用 Reader 的 close() 方法
// 因此只要一个 close() 调用即可
bufferedReader.close();
}
对象操作
序列化
序列化就是将一个对象转换成字节序列,方便存储和传输。
- 序列化: ObjectOutputStream.writeObject()
- 反序列化: ObjectInputStream.readObject()
不会对静态变量进行序列化,因为序列化只是保存对象的状态,静态变量属于类的状态。
Serializable
序列化的类需要实现 Serializable 接口,它只是一个标准,没有任何方法需要实现,但是如果不去实现它的话而进行序列化,会抛出异常。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
A a1 = new A(123, "abc");
String objectFile = "file/a1";
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(objectFile));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(a1);
objectOutputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(objectFile));
A a2 = (A) objectInputStream.readObject();
objectInputStream.close();
System.out.println(a2);
}
private static class A implements Serializable {
private int x;
private String y;
A(int x, String y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "x = " + x + " " + "y = " + y;
}
}
transient
transient 关键字可以使一些属性不会被序列化。
ArrayList 中存储数据的数组 elementData 是用 transient 修饰的,因为这个数组是动态扩展的,并不是所有的空间都被使用,因此就不需要所有的内容都被序列化。通过重写序列化和反序列化方法,使得可以只序列化数组中有内容的那部分数据。
private transient Object[] elementData;
网络操作
Java 中的网络支持:
- InetAddress: 用于表示网络上的硬件资源,即 IP 地址;
- URL: 统一资源定位符;
- Sockets: 使用 TCP 协议实现网络通信;
- Datagram: 使用 UDP 协议实现网络通信。
InetAddress
没有公有的构造函数,只能通过静态方法来创建实例。
InetAddress.getByName(String host);
InetAddress.getByAddress(byte[] address);
URL
可以直接从 URL 中读取字节流数据。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
/* 字节流 */
InputStream is = url.openStream();
/* 字符流 */
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "utf-8");
/* 提供缓存功能 */
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
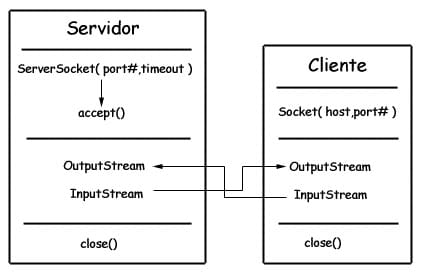
Sockets
- ServerSocket: 服务器端类
- Socket: 客户端类
- 服务器和客户端通过 InputStream 和 OutputStream 进行输入输出。
Datagram
- DatagramSocket: 通信类
- DatagramPacket: 数据包类
八、参考资料
- Eckel B, 埃克尔, 昊鹏, 等. Java 编程思想 [M]. 机械工业出版社, 2002.
- IBM: NIO 入门
- IBM: 深入分析 Java I/O 的工作机制
- IBM: 深入分析 Java 中的中文编码问题
- IBM: Java 序列化的高级认识
- NIO 与传统 IO 的区别
- Decorator Design Pattern
- Socket Multicast