Tomcat - Request请求处理过程:Connector
本文主要介绍request请求的处理过程。
引入
线程池Executor是在哪里启动的?
Request是如何处理并交个Container处理的?
Tomcat支持哪些协议?这些协议是处理的?协议层次结构如何设计的?
Connector
Connector构造
本质是初始化了ProtocolHandler,默认是HTTP/1.1 NIO实现。
/**
* Defaults to using HTTP/1.1 NIO implementation.
*/
public Connector() {
this("HTTP/1.1");
}
public Connector(String protocol) {
boolean apr = AprStatus.isAprAvailable() &&
AprStatus.getUseAprConnector();
ProtocolHandler p = null;
try {
p = ProtocolHandler.create(protocol, apr);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e);
}
if (p != null) {
protocolHandler = p;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocolHandler.getClass().getName();
} else {
protocolHandler = null;
protocolHandlerClassName = protocol;
}
// Default for Connector depends on this system property
setThrowOnFailure(Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"));
}
ProtocolHandler是怎么通过protocol初始化实现的呢?我们看下ProtocolHandler.create(protocol, apr)
public static ProtocolHandler create(String protocol, boolean apr)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
if (protocol == null || "HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol)
|| (!apr && org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))
|| (apr && org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))) {
if (apr) {
return new org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol();
} else {
return new org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol();
}
} else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)
|| (!apr && org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))
|| (apr && org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol.class.getName().equals(protocol))) {
if (apr) {
return new org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol();
} else {
return new org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol();
}
} else {
// Instantiate protocol handler
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocol);
return (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
}
}
我们看到上述方法实际通过Protocol初始化了ProtocolHandler, 我们看下它所支持的HTTP1.1,Ajp协议的处理,我们通过它的类层次结构来看协议支持处理类
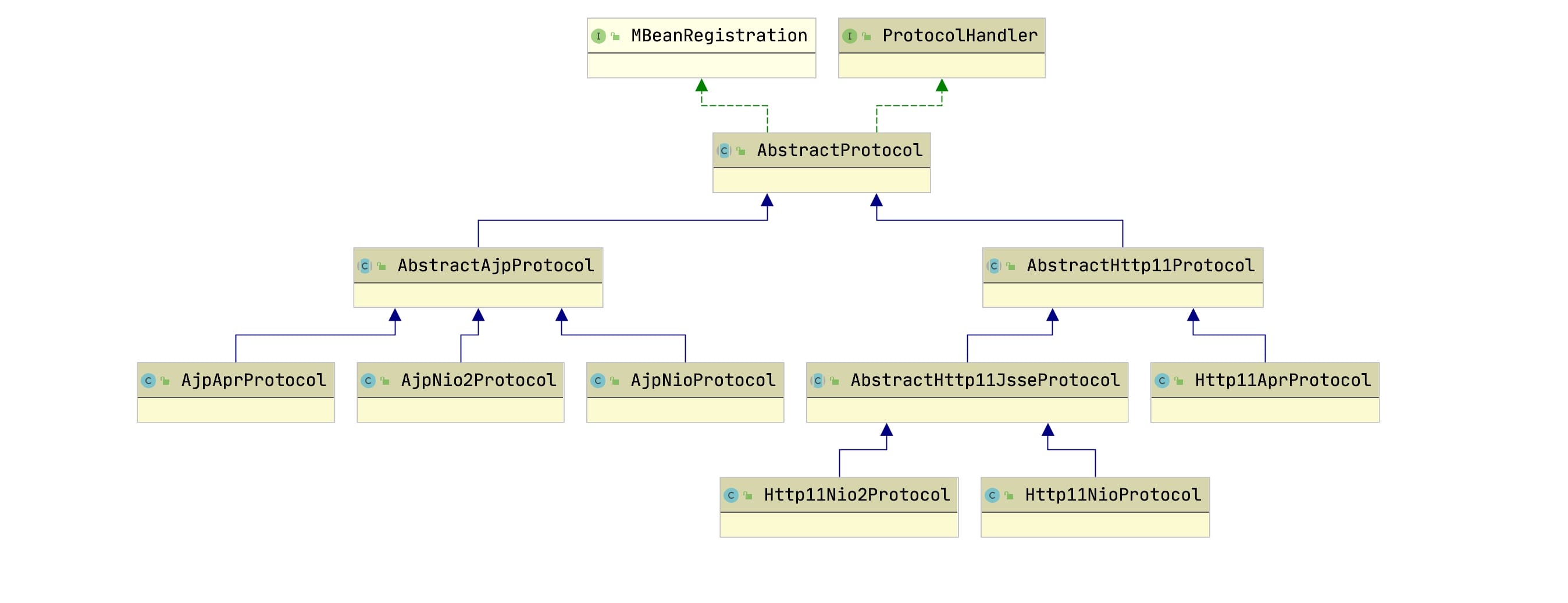
Connector初始化
在JMX的初始化模板方法initInternal中,进行了Connector的初始化,它做了哪些事呢?
- 给protocolHandler初始化了adapter //这adapter是真正衔接Container处理的适配器,后文我们会有详解。
- 设置parseBody的方法,默认为POST方法
- 一些校验
- 调用protocolHandler的init
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
if (protocolHandler == null) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"));
}
// 初始化 adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter); // 交给protocolHandler
if (service != null) {
protocolHandler.setUtilityExecutor(service.getServer().getUtilityExecutor());
}
// 设置parseBody的方法,默认为POST
if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) {
setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods());
}
// 校验
if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprStatus.isInstanceCreated()) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprListener",
getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
}
if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprStatus.isAprAvailable()) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoAprLibrary",
getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
}
if (AprStatus.isAprAvailable() && AprStatus.getUseOpenSSL() &&
protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol) {
AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler =
(AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?>) protocolHandler;
if (jsseProtocolHandler.isSSLEnabled() &&
jsseProtocolHandler.getSslImplementationName() == null) {
// OpenSSL is compatible with the JSSE configuration, so use it if APR is available
jsseProtocolHandler.setSslImplementationName(OpenSSLImplementation.class.getName());
}
}
try {
// 调用protocolHandler的init
protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
}
}
protocolHandler的init做了什么?本质上调用了AbstractEndpoint的init方法
/**
* Endpoint that provides low-level network I/O - must be matched to the
* ProtocolHandler implementation (ProtocolHandler using NIO, requires NIO
* Endpoint etc.).
*/
private final AbstractEndpoint<S,?> endpoint;
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.init", getName()));
logPortOffset();
}
if (oname == null) {
// Component not pre-registered so register it
oname = createObjectName();
if (oname != null) {
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null);
}
}
if (this.domain != null) {
rgOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=" + getName());
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(
getHandler().getGlobal(), rgOname, null);
}
String endpointName = getName();
endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length()-1));
endpoint.setDomain(domain);
endpoint.init();
}
endpoint.init()做了什么呢?之前的版本中是直接调用bind方法,这里改成了bindWithCleanup, 变化点在于失败后的清理操作。
public final void init() throws Exception {
if (bindOnInit) {
bindWithCleanup(); // 看这里
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_INIT;
}
// 下面就是注册JMX,前文我们有讲
if (this.domain != null) {
// Register endpoint (as ThreadPool - historical name)
oname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=ThreadPool,name=\"" + getName() + "\"");
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null);
ObjectName socketPropertiesOname = new ObjectName(domain +
":type=SocketProperties,name=\"" + getName() + "\"");
socketProperties.setObjectName(socketPropertiesOname);
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(socketProperties, socketPropertiesOname, null);
for (SSLHostConfig sslHostConfig : findSslHostConfigs()) {
registerJmx(sslHostConfig);
}
}
}
bindWithCleanup()做了bind方法,如果绑定失败就回调unbind方法。
private void bindWithCleanup() throws Exception {
try {
bind();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Ensure open sockets etc. are cleaned up if something goes
// wrong during bind
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
unbind();
throw t;
}
}
bind()方法做了初始化ServerSocket和初始化ssl
/**
* Initialize the endpoint.
*/
@Override
public void bind() throws Exception {
initServerSocket();
setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(1));
// Initialize SSL if needed
initialiseSsl();
selectorPool.open(getName());
}
// Separated out to make it easier for folks that extend NioEndpoint to
// implement custom [server]sockets
protected void initServerSocket() throws Exception {
if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) {
serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 打开ServerSocket通道
socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket());
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(), getPortWithOffset());
serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount()); // 绑定到指定服务地址和端口,这样你才可以通过这个访问服务(处理请求)
} else {
// Retrieve the channel provided by the OS
Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel();
if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) {
serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel) ic;
}
if (serverSock == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited"));
}
}
serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior
}
Connector的启动
这里依然是调用JMX的模板方法startInternal方法, start方法本质就是委托给protocolHandler处理,调用它的start方法
/**
* Begin processing requests via this Connector.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if a fatal startup error occurs
*/
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate settings before starting
if (getPortWithOffset() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPortWithOffset())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
try {
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
}
protocolHandler.start()方法如下,它又交给endpoint进行start处理
@Override
public void start() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName()));
logPortOffset();
}
// 本质是调用endpoint的start方法
endpoint.start();
// 启动一个异步的线程,处理startAsyncTimeout方法,每隔60秒执行一次
monitorFuture = getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!isPaused()) {
startAsyncTimeout();
}
}
}, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
endpoint.start()就是调用startInternal方法。当然它会先检查是否绑定端口,没有绑定便执行bindWithCleanup方法
public final void start() throws Exception {
if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) {
bindWithCleanup();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
startInternal();
}
我们看下NIOEndPoint的startInternal方法做了啥
/**
* Start the NIO endpoint, creating acceptor, poller threads.
*/
@Override
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
if (socketProperties.getProcessorCache() != 0) {
processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
}
if (socketProperties.getEventCache() != 0) {
eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getEventCache());
}
if (socketProperties.getBufferPool() != 0) {
nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getBufferPool());
}
// 重点:创建了Executor
if (getExecutor() == null) {
createExecutor();
}
initializeConnectionLatch();
// Start poller thread
poller = new Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(poller, getName() + "-ClientPoller");
pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
startAcceptorThread();
}
}
createExecutor()方法如下,本质是创建一个ThreadPoolExecutor
public void createExecutor() {
internalExecutor = true;
TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue();
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority());
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf);
taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor);
}