Tomcat - Container容器之Engine:StandardEngine
上文已经知道Container的整体结构和设计,其中Engine其实就是Servlet Engine,负责处理request的顶层容器。@pdai
理解思路
- 第一:抓住StandardEngine整体类依赖结构来理解
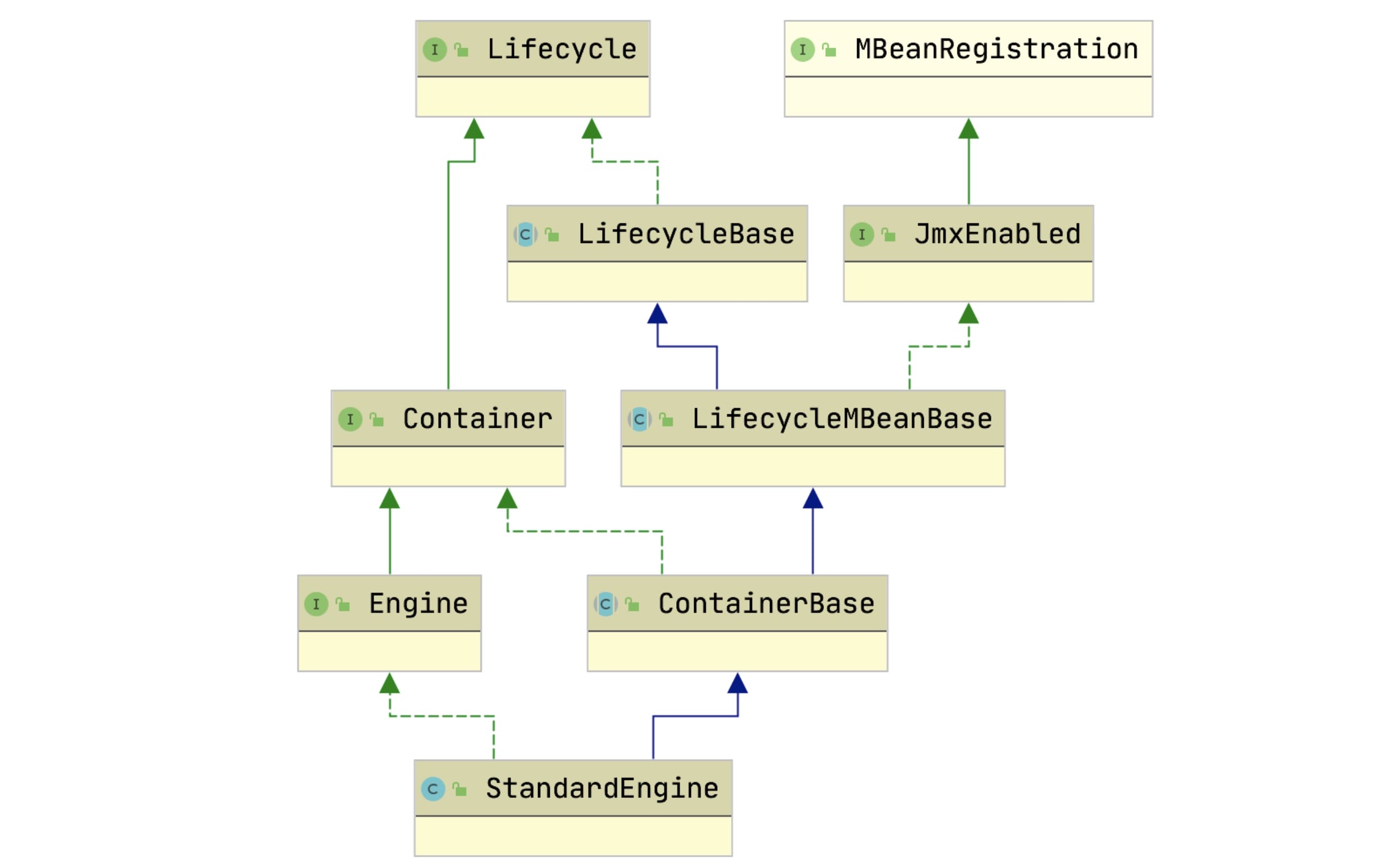
- 第二:结合server.xml中Engine配置来理解
见下文具体阐述。
- 第三:结合Engine Config官方配置文档
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/config/engine.html
Engine接口设计
这看Engine.java接口前,先要看下相关属性
- 支持设置的属性列表
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| backgroundProcessorDelay | 此值表示在此引擎及其子容器(包括所有Host和Context)上调用backgroundProcess方法之间的延迟(以秒为单位)。如果子容器的延迟值不为负(则表示它们正在使用自己的处理线程),则不会调用它们。将此值设置为正值将导致产生线程。等待指定的时间后,线程将在此引擎及其所有子容器上调用backgroundProcess方法。如果未指定,则此属性的默认值为10,表示10秒的延迟。 |
| className | 使用的Java类名称。此类必须实现org.apache.catalina.Engine接口。如果未指定,将使用标准值(定义如下)。 |
| defaultHost | 默认的主机名,它标识Host将处理针对主机名此服务器上的请求,但在此配置文件中没有配置。此名称必须与嵌套在name 其中的Host元素之一的属性匹配。 |
| jvmRoute | 必须在负载平衡方案中使用的标识符才能启用会话亲缘关系。标识符(在参与集群的所有Tomcat服务器之间必须是唯一的)将附加到生成的会话标识符上,因此允许前端代理始终将特定会话转发到同一Tomcat实例。注意,jvmRoute也可以使用jvmRoutesystem属性设置 。属性中的jvmRoute set<Engine>将覆盖任何jvmRoute系统属性。 |
| name | 此引擎的逻辑名称,用于日志和错误消息。在同一台Server中使用多个Service元素时 ,必须为每个引擎分配一个唯一的名称。 |
| startStopThreads | 该引擎将用来并行启动子Host元素的线程数。特殊值0将导致使用该值 Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()。Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + value除非小于1,否则将使用负值, 在这种情况下将使用1个线程。如果未指定,将使用默认值1。如果使用了1个线程,那么ExecutorService将使用当前线程,而不是使用。 |
- Engine的接口设计
这里你会发现,如下接口中包含上述defaultHost和jvmRoute属性设置;同时还有Service,因为Engine的上层是service。
/**
* An <b>Engine</b> is a Container that represents the entire Catalina servlet
* engine. It is useful in the following types of scenarios:
* <ul>
* <li>You wish to use Interceptors that see every single request processed
* by the entire engine.
* <li>You wish to run Catalina in with a standalone HTTP connector, but still
* want support for multiple virtual hosts.
* </ul>
* In general, you would not use an Engine when deploying Catalina connected
* to a web server (such as Apache), because the Connector will have
* utilized the web server's facilities to determine which Context (or
* perhaps even which Wrapper) should be utilized to process this request.
* <p>
* The child containers attached to an Engine are generally implementations
* of Host (representing a virtual host) or Context (representing individual
* an individual servlet context), depending upon the Engine implementation.
* <p>
* If used, an Engine is always the top level Container in a Catalina
* hierarchy. Therefore, the implementation's <code>setParent()</code> method
* should throw <code>IllegalArgumentException</code>.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
*/
public interface Engine extends Container {
/**
* @return the default host name for this Engine.
*/
public String getDefaultHost();
/**
* Set the default hostname for this Engine.
*
* @param defaultHost The new default host
*/
public void setDefaultHost(String defaultHost);
/**
* @return the JvmRouteId for this engine.
*/
public String getJvmRoute();
/**
* Set the JvmRouteId for this engine.
*
* @param jvmRouteId the (new) JVM Route ID. Each Engine within a cluster
* must have a unique JVM Route ID.
*/
public void setJvmRoute(String jvmRouteId);
/**
* @return the <code>Service</code> with which we are associated (if any).
*/
public Service getService();
/**
* Set the <code>Service</code> with which we are associated (if any).
*
* @param service The service that owns this Engine
*/
public void setService(Service service);
}
- 其它属性支持都包含在我们上文分析的ContainerBase中
/**
* The processor delay for this component.
*/
protected int backgroundProcessorDelay = -1;
/**
* The number of threads available to process start and stop events for any
* children associated with this container.
*/
private int startStopThreads = 1;
...
Engine接口实现:StandardEngine
接口中简单方法实现
上述接口里面的defaultHost, JvmRoute, service 很简单
/**
* Return the default host.
*/
@Override
public String getDefaultHost() {
return defaultHost;
}
/**
* Set the default host.
*
* @param host The new default host
*/
@Override
public void setDefaultHost(String host) {
String oldDefaultHost = this.defaultHost;
if (host == null) {
this.defaultHost = null;
} else {
this.defaultHost = host.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
}
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
service.getMapper().setDefaultHostName(host);
}
support.firePropertyChange("defaultHost", oldDefaultHost,
this.defaultHost);
}
/**
* Set the cluster-wide unique identifier for this Engine.
* This value is only useful in a load-balancing scenario.
* <p>
* This property should not be changed once it is set.
*/
@Override
public void setJvmRoute(String routeId) {
jvmRouteId = routeId;
}
/**
* Retrieve the cluster-wide unique identifier for this Engine.
* This value is only useful in a load-balancing scenario.
*/
@Override
public String getJvmRoute() {
return jvmRouteId;
}
/**
* Return the <code>Service</code> with which we are associated (if any).
*/
@Override
public Service getService() {
return this.service;
}
/**
* Set the <code>Service</code> with which we are associated (if any).
*
* @param service The service that owns this Engine
*/
@Override
public void setService(Service service) {
this.service = service;
}
child, parent
addChild重载方法,限制只能添加Host作为子容器;
setParent直接抛出异常,因为Engine接口中已经包含了setService方法作为它的上层,而Engine的上层没有容器的概念。
/**
* Add a child Container, only if the proposed child is an implementation
* of Host.
*
* @param child Child container to be added
*/
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (!(child instanceof Host))
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("standardEngine.notHost"));
super.addChild(child);
}
/**
* Disallow any attempt to set a parent for this Container, since an
* Engine is supposed to be at the top of the Container hierarchy.
*
* @param container Proposed parent Container
*/
@Override
public void setParent(Container container) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("standardEngine.notParent"));
}
Lifecycle的模板方法
无非就是调用上文中我们介绍ContainerBase中的方法
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Ensure that a Realm is present before any attempt is made to start
// one. This will create the default NullRealm if necessary.
getRealm();
super.initInternal();
}
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Log our server identification information
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardEngine.start", ServerInfo.getServerInfo()));
}
// Standard container startup
super.startInternal();
}
LogAccess
这里需要补充下之前没有介绍的日志访问,这里介绍下。
运行Web服务器时,正常生成的输出文件之一是访问日志,该访问日志以标准格式为服务器处理的每个请求生成一行信息。Catalina包括一个可选的Valve实现,该实现可以创建与Web服务器创建的标准格式相同的访问日志,也可以创建任意数量的自定义格式。
需要先看下xml配置; 您可以通过嵌套如下所示的Valve元素,要求Catalina为Engine, Host或Context处理的所有请求创建访问日志:
<Engine name="Standalone" ...>
...
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve"
prefix="catalina_access_log" suffix=".txt"
pattern="common"/>
...
</Engine>
好了看下具体的实现,使用适配器模式获取AccessLog类型的Valve:
适配器模式看这里:结构型 - 适配器(Adapter)
@Override
public AccessLog getAccessLog() {
if (accessLogScanComplete) {
return accessLog;
}
AccessLogAdapter adapter = null;
Valve valves[] = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (valve instanceof AccessLog) { // 看这里
if (adapter == null) {
adapter = new AccessLogAdapter((AccessLog) valve);
} else {
adapter.add((AccessLog) valve);
}
}
}
if (adapter != null) {
accessLog = adapter;
}
accessLogScanComplete = true;
return accessLog;
}
AccessLog(日志记录器)主要的作用就是记录日志,这个记录的方法就是logAccess()方法
/**
* Override the default implementation. If no access log is defined for the
* Engine, look for one in the Engine's default host and then the default
* host's ROOT context. If still none is found, return the default NoOp
* access log.
*/
@Override
public void logAccess(Request request, Response response, long time,
boolean useDefault) {
boolean logged = false;
// 如果有accessLog,则记录日志
if (getAccessLog() != null) {
accessLog.log(request, response, time);
logged = true;
}
// 没找到且使用useDefault,表示从下层容器中获取accessLog
if (!logged && useDefault) {
AccessLog newDefaultAccessLog = defaultAccessLog.get();
if (newDefaultAccessLog == null) {
// If we reached this point, this Engine can't have an AccessLog
// Look in the defaultHost
Host host = (Host) findChild(getDefaultHost()); // 如果没有默认的accessLog,则获取默认Host的accessLog
Context context = null;
if (host != null && host.getState().isAvailable()) {
newDefaultAccessLog = host.getAccessLog();
if (newDefaultAccessLog != null) {
if (defaultAccessLog.compareAndSet(null,
newDefaultAccessLog)) {
AccessLogListener l = new AccessLogListener(this,
host, null);
l.install(); // 注册AccessLog监听器至当前Engine
}
} else {
// Try the ROOT context of default host
context = (Context) host.findChild(""); // 如果仍然没有找到,则获取默认host的ROOT Context的accessLog
if (context != null &&
context.getState().isAvailable()) {
newDefaultAccessLog = context.getAccessLog();
if (newDefaultAccessLog != null) {
if (defaultAccessLog.compareAndSet(null,
newDefaultAccessLog)) {
AccessLogListener l = new AccessLogListener(
this, null, context);
l.install();
}
}
}
}
}
if (newDefaultAccessLog == null) {
newDefaultAccessLog = new NoopAccessLog(); // 这个其实是一个空模式,以便采用统一方式调用(不用判空了)
if (defaultAccessLog.compareAndSet(null,
newDefaultAccessLog)) {
AccessLogListener l = new AccessLogListener(this, host,
context);
l.install();
}
}
}
// 最后记录日志,(上面最后有空模式实现,所以可以直接调用,不用判空)
newDefaultAccessLog.log(request, response, time);
}
}
其中涉及的相关内部类如下:
protected static final class NoopAccessLog implements AccessLog {
@Override
public void log(Request request, Response response, long time) {
// NOOP
}
@Override
public void setRequestAttributesEnabled(
boolean requestAttributesEnabled) {
// NOOP
}
@Override
public boolean getRequestAttributesEnabled() {
// NOOP
return false;
}
}
protected static final class AccessLogListener
implements PropertyChangeListener, LifecycleListener,
ContainerListener {
private final StandardEngine engine;
private final Host host;
private final Context context;
private volatile boolean disabled = false;
public AccessLogListener(StandardEngine engine, Host host,
Context context) {
this.engine = engine;
this.host = host;
this.context = context;
}
public void install() {
engine.addPropertyChangeListener(this);
if (host != null) { // 同时注册至host和context
host.addContainerListener(this);
host.addLifecycleListener(this);
}
if (context != null) {
context.addLifecycleListener(this);
}
}
private void uninstall() {
disabled = true;
if (context != null) {
context.removeLifecycleListener(this);
}
if (host != null) {
host.removeLifecycleListener(this);
host.removeContainerListener(this);
}
engine.removePropertyChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) {
if (disabled) return;
String type = event.getType();
if (Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT.equals(type) ||
Lifecycle.BEFORE_STOP_EVENT.equals(type) ||
Lifecycle.BEFORE_DESTROY_EVENT.equals(type)) {
// Container is being started/stopped/removed
// Force re-calculation and disable listener since it won't
// be re-used
engine.defaultAccessLog.set(null);
uninstall();
}
}
@Override
public void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt) {
if (disabled) return;
if ("defaultHost".equals(evt.getPropertyName())) {
// Force re-calculation and disable listener since it won't
// be re-used
engine.defaultAccessLog.set(null);
uninstall();
}
}
@Override
public void containerEvent(ContainerEvent event) {
// Only useful for hosts
if (disabled) return;
if (Container.ADD_CHILD_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
Context context = (Context) event.getData();
if (context.getPath().isEmpty()) {
// Force re-calculation and disable listener since it won't
// be re-used
engine.defaultAccessLog.set(null);
uninstall();
}
}
}
}
JMX相关
之前已经有过相关介绍,这里不再介绍相关方法,只列出相关方法:
@Override
protected String getObjectNameKeyProperties() {
return "type=Engine";
}
@Override
protected String getDomainInternal() {
return getName();
}