SpringBoot定时任务 - Spring Schedule实现方式
前文我们介绍了Timer和ScheduledExecutorService是JDK内置的定时任务方案以及Netty内部基于时间轮实现的HashedWheelTimer;而主流的SpringBoot集成方案有两种,一种是Spring Sechedule, 另一种是Spring集成Quartz; 本文主要介绍Spring Schedule实现方式。@pdai
准备知识点
cron表达式, 以及BeanPostProcessor(方便你理解它的原理,相关介绍在之前的文章中Spring核心之控制反转(IOC)源码解析).
什么是cron表达式
定时任务和CRON表达式在开发中使用也非常广泛;在学习时,总体上理解,对常用的知悉,开发时可以快速查询使用即可。
相关文章
- CRON表达式 - CRON表达式介绍和使用
- 定时任务和CRON表达式在开发中使用也非常广泛,本文整理了CRON表达式和常见使用例子
- CRON表达式 - CRON生成和校验工具
- 本文主要总结常用的在线CRON生成和校验工具,从而高效的写出正确的表达式
实现案例
SpringTask封装的比较好,使用非常简单。
@EnableScheduling+@Scheduled
- 通过@EnableScheduling启用定时任务,@Scheduled定义任务
@EnableScheduling
@Configuration
public class ScheduleDemo {
/**
* 每隔1分钟执行一次。
*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000 * 60 * 1)
public void runScheduleFixedRate() {
log.info("runScheduleFixedRate: current DateTime, {}", LocalDateTime.now());
}
/**
* 每个整点小时执行一次。
*/
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 */1 * * ?")
public void runScheduleCron() {
log.info("runScheduleCron: current DateTime, {}", LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
- @Scheduled所支持的参数:
cron:cron表达式,指定任务在特定时间执行;fixedDelay:表示上一次任务执行完成后多久再次执行,参数类型为long,单位ms;fixedDelayString:与fixedDelay含义一样,只是参数类型变为String;fixedRate:表示按一定的频率执行任务,参数类型为long,单位ms;fixedRateString: 与fixedRate的含义一样,只是将参数类型变为String;initialDelay:表示延迟多久再第一次执行任务,参数类型为long,单位ms;initialDelayString:与initialDelay的含义一样,只是将参数类型变为String;zone:时区,默认为当前时区,一般没有用到。
进一步理解
我们再通过一些问题来帮助你更深入理解SpringTask实现方式。@pdai
使用Spring Schedule要注意什么?
- 关于异常处理
建议自行处理异常
- 关于超时处理
在实际的开发中,这个问题经常会出现,比如执行一段时间后定时任务不再执行了; 这种情况会发生在,比如你调用一个第三方接口,没有设置调用超时,继而引发异常,这时候当前任务便阻塞了。
SpringTask的原理?
SpringTask的源码在这里:
@EnableScheduling注解
添加@EnableScheduling注解会自动注入SchedulingConfiguration
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
* @see Scheduled
* @see SchedulingConfiguration
* @see SchedulingConfigurer
* @see ScheduledTaskRegistrar
* @see Trigger
* @see ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(SchedulingConfiguration.class)
@Documented
public @interface EnableScheduling {
}
SchedulingConfiguration中初始化ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
SchedulingConfiguration配置中自动初始化ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class SchedulingConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.SCHEDULED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor scheduledAnnotationProcessor() {
return new ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
}
}
什么是BeanPostProcessor? 我们在前文中有详解的讲解,具体看Spring核心之控制反转(IOC)源码解析
Spring 容器中 Bean 的生命周期流程

ScheduledTaskRegistrar注册task
在ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor构造函数中初始化了ScheduledTaskRegistrar
/**
* Create a default {@code ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}.
*/
public ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
this.registrar = new ScheduledTaskRegistrar();
}
ScheduledTaskRegistrar最主要的是注册各种类型的task (这种方式在新的版本中已经废弃了)
protected void scheduleTasks() {
if (this.taskScheduler == null) {
this.localExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
this.taskScheduler = new ConcurrentTaskScheduler(this.localExecutor);
}
if (this.triggerTasks != null) {
for (TriggerTask task : this.triggerTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleTriggerTask(task));
}
}
if (this.cronTasks != null) {
for (CronTask task : this.cronTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleCronTask(task));
}
}
if (this.fixedRateTasks != null) {
for (IntervalTask task : this.fixedRateTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleFixedRateTask(task));
}
}
if (this.fixedDelayTasks != null) {
for (IntervalTask task : this.fixedDelayTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleFixedDelayTask(task));
}
}
}
注册哪些Task,怎么设计类的呢?
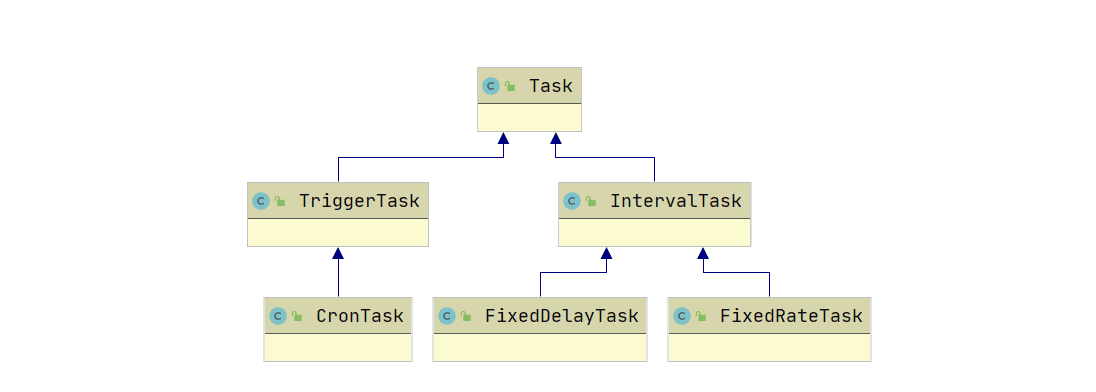
ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor加载Scheduled注解
在BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization阶段加载Scheduled注解
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean || bean instanceof TaskScheduler ||
bean instanceof ScheduledExecutorService) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
Class<?> targetClass = AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(bean);
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetClass) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetClass, Arrays.asList(Scheduled.class, Schedules.class))) {
Map<Method, Set<Scheduled>> annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetClass,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<Set<Scheduled>>) method -> {
Set<Scheduled> scheduledAnnotations = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedRepeatableAnnotations(
method, Scheduled.class, Schedules.class);
return (!scheduledAnnotations.isEmpty() ? scheduledAnnotations : null);
});
if (annotatedMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetClass);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @Scheduled annotations found on bean class: " + targetClass);
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
annotatedMethods.forEach((method, scheduledAnnotations) ->
scheduledAnnotations.forEach(scheduled -> processScheduled(scheduled, method, bean)));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(annotatedMethods.size() + " @Scheduled methods processed on bean '" + beanName +
"': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
return bean;
}
Scheduled注解是添加到方法级别,具体如下
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(Schedules.class)
public @interface Scheduled {
/**
* A special cron expression value that indicates a disabled trigger: {@value}.
* <p>This is primarily meant for use with <code>${...}</code> placeholders,
* allowing for external disabling of corresponding scheduled methods.
* @since 5.1
* @see ScheduledTaskRegistrar#CRON_DISABLED
*/
String CRON_DISABLED = ScheduledTaskRegistrar.CRON_DISABLED;
/**
* A cron-like expression, extending the usual UN*X definition to include triggers
* on the second, minute, hour, day of month, month, and day of week.
* <p>For example, {@code "0 * * * * MON-FRI"} means once per minute on weekdays
* (at the top of the minute - the 0th second).
* <p>The fields read from left to right are interpreted as follows.
* <ul>
* <li>second</li>
* <li>minute</li>
* <li>hour</li>
* <li>day of month</li>
* <li>month</li>
* <li>day of week</li>
* </ul>
* <p>The special value {@link #CRON_DISABLED "-"} indicates a disabled cron
* trigger, primarily meant for externally specified values resolved by a
* <code>${...}</code> placeholder.
* @return an expression that can be parsed to a cron schedule
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronExpression#parse(String)
*/
String cron() default "";
/**
* A time zone for which the cron expression will be resolved. By default, this
* attribute is the empty String (i.e. the server's local time zone will be used).
* @return a zone id accepted by {@link java.util.TimeZone#getTimeZone(String)},
* or an empty String to indicate the server's default time zone
* @since 4.0
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronTrigger#CronTrigger(String, java.util.TimeZone)
* @see java.util.TimeZone
*/
String zone() default "";
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period between the end of the
* last invocation and the start of the next.
* <p>The time unit is milliseconds by default but can be overridden via
* {@link #timeUnit}.
* @return the delay
*/
long fixedDelay() default -1;
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period between the end of the
* last invocation and the start of the next.
* <p>The time unit is milliseconds by default but can be overridden via
* {@link #timeUnit}.
* @return the delay as a String value — for example, a placeholder
* or a {@link java.time.Duration#parse java.time.Duration} compliant value
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String fixedDelayString() default "";
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period between invocations.
* <p>The time unit is milliseconds by default but can be overridden via
* {@link #timeUnit}.
* @return the period
*/
long fixedRate() default -1;
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period between invocations.
* <p>The time unit is milliseconds by default but can be overridden via
* {@link #timeUnit}.
* @return the period as a String value — for example, a placeholder
* or a {@link java.time.Duration#parse java.time.Duration} compliant value
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String fixedRateString() default "";
/**
* Number of units of time to delay before the first execution of a
* {@link #fixedRate} or {@link #fixedDelay} task.
* <p>The time unit is milliseconds by default but can be overridden via
* {@link #timeUnit}.
* @return the initial
* @since 3.2
*/
long initialDelay() default -1;
/**
* Number of units of time to delay before the first execution of a
* {@link #fixedRate} or {@link #fixedDelay} task.
* <p>The time unit is milliseconds by default but can be overridden via
* {@link #timeUnit}.
* @return the initial delay as a String value — for example, a placeholder
* or a {@link java.time.Duration#parse java.time.Duration} compliant value
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String initialDelayString() default "";
/**
* The {@link TimeUnit} to use for {@link #fixedDelay}, {@link #fixedDelayString},
* {@link #fixedRate}, {@link #fixedRateString}, {@link #initialDelay}, and
* {@link #initialDelayString}.
* <p>Defaults to {@link TimeUnit#MICROSECONDS}.
* <p>This attribute is ignored for {@linkplain #cron() cron expressions}
* and for {@link java.time.Duration} values supplied via {@link #fixedDelayString},
* {@link #fixedRateString}, or {@link #initialDelayString}.
* @return the {@code TimeUnit} to use
* @since 5.3.10
*/
TimeUnit timeUnit() default TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS;
}
@Scheduled所支持的参数:
cron:cron表达式,指定任务在特定时间执行;fixedDelay:表示上一次任务执行完成后多久再次执行,参数类型为long,单位ms;fixedDelayString:与fixedDelay含义一样,只是参数类型变为String;fixedRate:表示按一定的频率执行任务,参数类型为long,单位ms;fixedRateString: 与fixedRate的含义一样,只是将参数类型变为String;initialDelay:表示延迟多久再第一次执行任务,参数类型为long,单位ms;initialDelayString:与initialDelay的含义一样,只是将参数类型变为String;zone:时区,默认为当前时区,一般没有用到。
获取到方法上Scheduled注解(对任务的定义),通过processScheduled处理具体类型的task
/**
* Process the given {@code @Scheduled} method declaration on the given bean.
* @param scheduled the {@code @Scheduled} annotation
* @param method the method that the annotation has been declared on
* @param bean the target bean instance
* @see #createRunnable(Object, Method)
*/
protected void processScheduled(Scheduled scheduled, Method method, Object bean) {
try {
Runnable runnable = createRunnable(bean, method);
boolean processedSchedule = false;
String errorMessage =
"Exactly one of the 'cron', 'fixedDelay(String)', or 'fixedRate(String)' attributes is required";
Set<ScheduledTask> tasks = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
// Determine initial delay
long initialDelay = convertToMillis(scheduled.initialDelay(), scheduled.timeUnit());
String initialDelayString = scheduled.initialDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(initialDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay < 0, "Specify 'initialDelay' or 'initialDelayString', not both");
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
initialDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(initialDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initialDelayString)) {
try {
initialDelay = convertToMillis(initialDelayString, scheduled.timeUnit());
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid initialDelayString value \"" + initialDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
}
}
// Check cron expression
String cron = scheduled.cron();
if (StringUtils.hasText(cron)) {
String zone = scheduled.zone();
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
cron = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(cron);
zone = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(zone);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(cron)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay == -1, "'initialDelay' not supported for cron triggers");
processedSchedule = true;
if (!Scheduled.CRON_DISABLED.equals(cron)) {
TimeZone timeZone;
if (StringUtils.hasText(zone)) {
timeZone = StringUtils.parseTimeZoneString(zone);
}
else {
timeZone = TimeZone.getDefault();
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleCronTask(new CronTask(runnable, new CronTrigger(cron, timeZone))));
}
}
}
// At this point we don't need to differentiate between initial delay set or not anymore
if (initialDelay < 0) {
initialDelay = 0;
}
// Check fixed delay
long fixedDelay = convertToMillis(scheduled.fixedDelay(), scheduled.timeUnit());
if (fixedDelay >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedDelayString = scheduled.fixedDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedDelayString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedDelay = convertToMillis(fixedDelayString, scheduled.timeUnit());
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedDelayString value \"" + fixedDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
}
// Check fixed rate
long fixedRate = convertToMillis(scheduled.fixedRate(), scheduled.timeUnit());
if (fixedRate >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedRateString = scheduled.fixedRateString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedRateString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedRateString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedRateString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedRateString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedRate = convertToMillis(fixedRateString, scheduled.timeUnit());
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedRateString value \"" + fixedRateString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
}
// Check whether we had any attribute set
Assert.isTrue(processedSchedule, errorMessage);
// Finally register the scheduled tasks
synchronized (this.scheduledTasks) {
Set<ScheduledTask> regTasks = this.scheduledTasks.computeIfAbsent(bean, key -> new LinkedHashSet<>(4));
regTasks.addAll(tasks);
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Encountered invalid @Scheduled method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
ScheduledTaskRegistrar 中解析task
以CronTask为例,如果定义了taskScheduler则由taskScheduler执行,如果没有放到unresolvedTasks中。
/**
* Schedule the specified cron task, either right away if possible
* or on initialization of the scheduler.
* @return a handle to the scheduled task, allowing to cancel it
* (or {@code null} if processing a previously registered task)
* @since 4.3
*/
@Nullable
public ScheduledTask scheduleCronTask(CronTask task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.unresolvedTasks.remove(task);
boolean newTask = false;
if (scheduledTask == null) {
scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask(task);
newTask = true;
}
if (this.taskScheduler != null) {
scheduledTask.future = this.taskScheduler.schedule(task.getRunnable(), task.getTrigger());
}
else {
addCronTask(task);
this.unresolvedTasks.put(task, scheduledTask);
}
return (newTask ? scheduledTask : null);
}
TaskScheduler对Task处理
默认是ConcurrentTaskScheduler, 处理方法如下
@Override
@Nullable
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Trigger trigger) {
try {
if (this.enterpriseConcurrentScheduler) {
return new EnterpriseConcurrentTriggerScheduler().schedule(decorateTask(task, true), trigger);
}
else {
ErrorHandler errorHandler =
(this.errorHandler != null ? this.errorHandler : TaskUtils.getDefaultErrorHandler(true));
return new ReschedulingRunnable(task, trigger, this.clock, this.scheduledExecutor, errorHandler).schedule();
}
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + this.scheduledExecutor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
EnterpriseConcurrentTriggerScheduler 是 JSR-236 Trigger标准,它的处理方法如下
/**
* Delegate that adapts a Spring Trigger to a JSR-236 Trigger.
* Separated into an inner class in order to avoid a hard dependency on the JSR-236 API.
*/
private class EnterpriseConcurrentTriggerScheduler {
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, final Trigger trigger) {
ManagedScheduledExecutorService executor = (ManagedScheduledExecutorService) scheduledExecutor;
return executor.schedule(task, new javax.enterprise.concurrent.Trigger() {
@Override
@Nullable
public Date getNextRunTime(@Nullable LastExecution le, Date taskScheduledTime) {
return (trigger.nextExecutionTime(le != null ?
new SimpleTriggerContext(le.getScheduledStart(), le.getRunStart(), le.getRunEnd()) :
new SimpleTriggerContext()));
}
@Override
public boolean skipRun(LastExecution lastExecution, Date scheduledRunTime) {
return false;
}
});
}
}
如果没有使用EnterpriseConcurrentTriggerScheduler, 则使用ReschedulingRunnable,本质上由ScheduledExecutorService处理
public ReschedulingRunnable(Runnable delegate, Trigger trigger, Clock clock,
ScheduledExecutorService executor, ErrorHandler errorHandler) {
super(delegate, errorHandler);
this.trigger = trigger;
this.triggerContext = new SimpleTriggerContext(clock);
this.executor = executor;
}
@Nullable
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule() {
synchronized (this.triggerContextMonitor) {
this.scheduledExecutionTime = this.trigger.nextExecutionTime(this.triggerContext);
if (this.scheduledExecutionTime == null) {
return null;
}
long initialDelay = this.scheduledExecutionTime.getTime() - this.triggerContext.getClock().millis();
this.currentFuture = this.executor.schedule(this, initialDelay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this;
}
}
示例源码
https://github.com/realpdai/tech-pdai-spring-demos